
- #Findstr windows find file how to
- #Findstr windows find file install
- #Findstr windows find file license
- #Findstr windows find file series
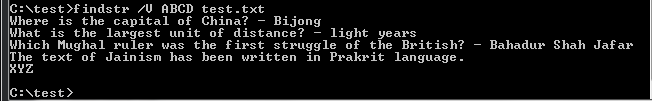
Note that this line uses the following syntax explained in the previous post on ‘for’: As often as not, I also use ‘find /v’, returning the lines that don’t match the specified string.įor example, if you have a control file listing servers in several geographic locations, but you are only interested in processing servers in ‘bne’ (case insensitive with ‘/i’), you could run:Ĭombined with a ‘for’ command, this could be:įor /f "skip=2" %i in ('find /i "bne" c:\temp\control.txt') do echo %i I usually use find because more often than not I want to filter a string literal – a specific word or combination of characters – from an input string. Help on each is available from the command prompt with the ‘/?’ argument. These two commands are crucial in efficient ‘for’ loop processing, invaluable when filtering a control file or the results of an in-line command. These components are the for, find, findstr, set, if and echo commands, control files used to control data input, combined with errorlevels, command concatenation, nested loops and if/then/else constructs.ĭescribed in this post are the ‘find’ and ‘findstr’ commands - unless you want to spend all your time manually creating or filtering control files you will often use these commands when constructing repeatable command-lines.
#Findstr windows find file series
This certificate can then be used to send encrypted email to this person.This is the second in a series of posts containing information on what I consider the building blocks to automate repetitive tasks at the Windows command-line.
#Findstr windows find file install
When you receive a signed email, the app provides a feature to install corresponding encryption certificate on your device if the certificate is available. Install certificates from a received message Your smartcard may also require a PIN to access the certificate. If your certificate is stored on a smartcard, you'll be prompted to insert the smartcard to read the message. If there's a certificate available, the message is decrypted when you open it. When you receive an encrypted message, the mail app checks whether there's a certificate available on your computer. Use Sign and Encrypt icons to turn on digital signature and encryption for this message While composing a message, select Options from the ribbon The option to sign or encrypt can be changed for individual messages, unless EAS policies prevent it. (Optional) Select Always sign with S/MIME, Always encrypt with S/MIME, or both, to automatically digitally sign or encrypt all outgoing messages
#Findstr windows find file how to

Valid Personal Information Exchange (PFX) certificates are installed on the device.Users can't use S/MIME signing and encryption with a personal account such as S/MIME is enabled for Exchange accounts (on-premises and Exchange Online).
#Findstr windows find file license
The following table lists the Windows editions that support Email Encryption (S/MIME): Windows ProĮmail Encryption (S/MIME) license entitlements are granted by the following licenses: Windows Pro/Pro Education/SEįor more information about Windows licensing, see Windows licensing overview. Windows edition and licensing requirements Recipients can only verify the digital signature if they're using an email client that supports S/MIME. Digital signaturesĪ digitally signed message reassures the recipient that the message hasn't been tampered with, and verifies the identity of the sender. If you try to send an encrypted message to recipients whose encryption certificate isn't available, the app prompts you to remove these recipients before sending the email. Users can only read encrypted messages if the message is received on their Exchange account, and they have corresponding decryption keys.Įncrypted messages can be read only by recipients who have a certificate. Users can send encrypted message to recipients that have an encryption certificate. Users can digitally sign a message, which provides the recipients with a way to verify the identity of the sender and that the message hasn't been tampered with. To read the messages, recipients must have a digital identification (ID), also known as a certificate.
S/MIME enables users to encrypt outgoing messages and attachments so that only intended recipients can read them.
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) provides an added layer of security for email sent to and from an Exchange ActiveSync (EAS) account.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
